Mumbai needs to wake up and save the 5K acres of mangroves under serious threat
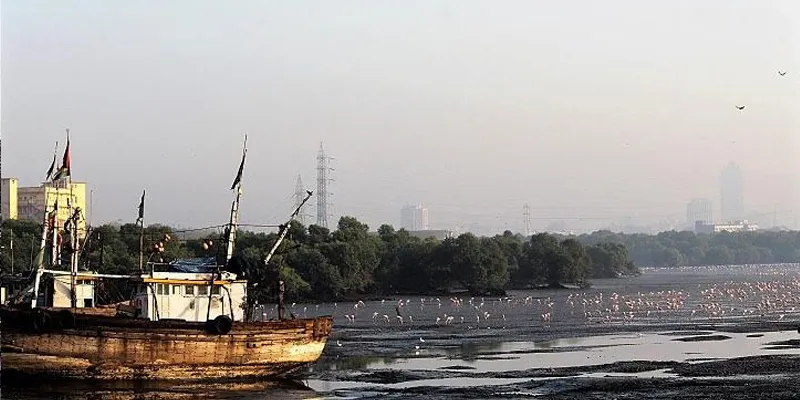
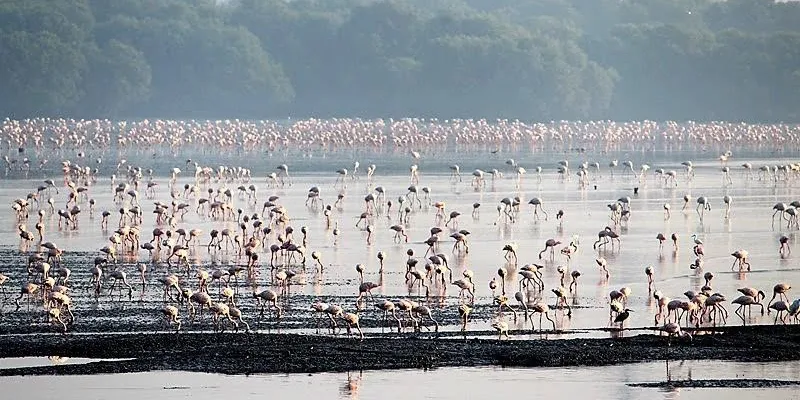
The Sewri wetland is known for many winged visitors including flamingos that come for blue-green algae annually. It is under threat, thanks to rapid urbanisation.

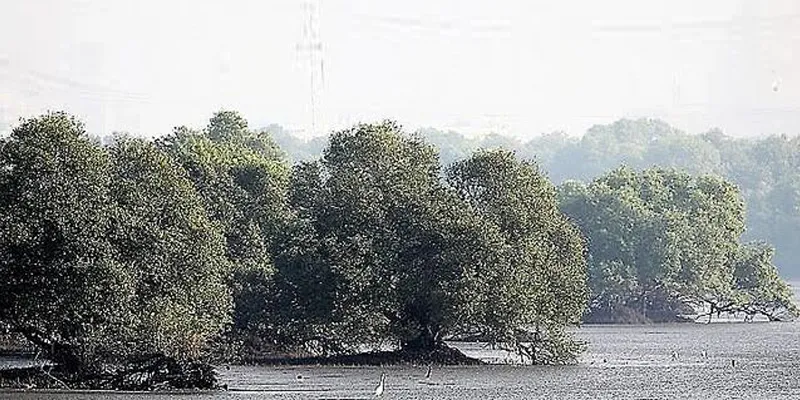
Mangroves form an integral part of the landscape of Mumbai and are essential in maintaining the stability of the coastline. Apart from serving as breeding and feeding grounds for birds, reptiles, amphibians, mammals, as well as humans, they prevent erosion, protect the coasts from disasters, and decrease the effect of water pollution on the coastlines.
Around 5,000 acres of mangrove swamps are spread over areas like Mahim, Madh, Thane creek, Versova, Gorai, and Ghodbunder in Mumbai. They are under serious threat with as high as 40 percent of the land being lost to reclamation for development projects.
The Sewri wetland—a crescent-shaped stretch of mangroves and open mudflats between Sewri and Trombay covering an area of 10 km in length and 3 km in width—is unique for its mudflats and the extraordinary range of biodiversity it sustains. Mudflats are coastal wetlands formed by the deposition of mud, silt, animal detritus, and clay due to tidal activity. Most of the mudflats lie within the intertidal zone and they get submerged and exposed twice a day based on the tide timings.
The wetland provides an ideal winter feeding ground for two of the five species of flamingos—the lesser and greater flamingos—that regularly come to the site for feeding. The flamingos start arriving by the end of October from the Rann of Kutch in Gujarat and go back when the monsoon hits Mumbai in June. The birds share a symbiotic relationship with the mangroves—while the mangroves provide food and shelter for the birds, their excrement helps in the growth of the mangroves.
The Sewri mudflats are known to have the largest congregation of lesser flamingos at a single spot and the numbers have grown over the last couple of years. These pink visitors have attracted attention since they first started arriving in the 1990s.
It is not only the flamingos but a range of bird species—150 of them—that continue to survive on the Sewri mudflats. A five-year-long study by the Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS) has found that close to 40,000 flamingos and five lakh waders (birds that wade in shallow water in search of food) visit the wetland. The BNHS and BirdLife International have declared the site an Important Bird Area (IBA) in 2004 as the area also has incredible floral biodiversity with 10 species of mangroves, 13 mangrove-associated species, 53 seed-bearing plant species, as well as many types of crustaceans, molluscs, and algae.
Although Sewri has remained relatively untouched because it comes under the security blanket of the Port Trust, threats to the mudflats come in various forms such as:
- Encroachment by slums
- Pollution from industries (chemicals, oil, grease, pesticides)
- Poaching of birds
- Fuelwood collection from mangroves
- Electrocution of flamingos on high-tension wires.
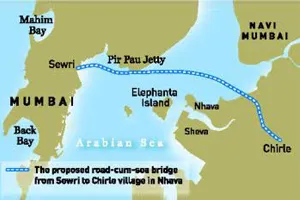
The biggest threat to the wetland in recent years has come from city expansion with the proposed plan to build the Rs 8,500-crore Sewri-Nhava Sheva trans-harbour link that includes a 22-km road-cum-sea bridge that will link Sewri on the Mumbai island to a village—Chirle—on the Nhava Sheva mainland.
This will be a six-lane road, 16.5 km of which will be a sea bridge and will also include an independent twin-track metro in its second phase. And this bridge will run through the Sewri mudflats!
Environmentalists and conservationists claim that the project violates Coastal Regulation Zone rules. To save this habitat, the BNHS brought out a report on the birds in the area and suggested that the bridge needs to be moved or shifted 500m to the south to save the bird habitat. The society submitted it to the Mumbai Metropolitan Region Development Authority (MMRDA), the state government entity implementing the project, but to no avail.
The latest news coming from the site suggests that the MMRDA has now resurrected the project and has received environmental clearance for the construction activity. This not only spells doom for the biodiversity of the area but could also pose a threat to the winged visitors and change their migration behaviour.
Considering its unique but threatened status, the state forest department has sent a proposal to the Ministry of Environment and Forests to declare Sewri creek a Ramsar site in 2013. If the proposal is accepted, it will be among the first few Ramsar sites from Maharashtra to be included in the list of Ramsar sites across the nation and could save the wetland from further deterioration.
The BNHS conducts regular walks to Sewri so that people can learn about the wetlands while enjoying the beautiful sight of the flamingos.









Disclaimer: This article, authored by Aarti Kelkar-Khambete, was first published on India Water Portal.







