Google's 'sticky' way of reducing road accidents
Google today had a fresh US patent for a sticky coating that could be applied to self-driving cars so pedestrians stick instead of bouncing off when hit.

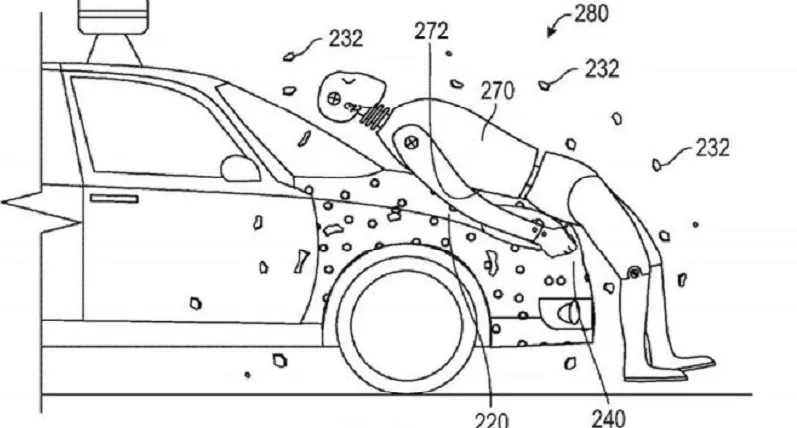
The patent describes a layer of adhesive on a car's hood, front bumper and possibly front side panels sealed with a coating that, when broken, would bare a gluey surface akin to fly paper modified to catch humans. Upon impact with a pedestrian, the coating is broken exposing the adhesive layer, read patent paperwork dated May 17 and listing the applicant as Google.
The adhesive bonds the pedestrian to the vehicle so that the pedestrian remains with the vehicle until it stops, and is not thrown from the vehicle, thereby preventing a secondary impact between the pedestrian and the road surface or other object.
Google reasoned in the patent application that pedestrians hit by cars typically suffer further injury by being knocked or hurled to the pavement or other objects. Self-driving cars could hit roads within five years, the head of Fiat Chrysler Automobiles said earlier this month, shortly after the company announced an alliance with Google parent Alphabet.
Chief executive Sergio Marchionne declined to disclose financial details of the partnership or a timetable for building minivans that will expand the Internet company's test fleet of autonomous vehicles.
It's not sort of 'pie-in-the-sky,' the thing is real and it's coming, people are talking about 20 years, I think we'll have it here in the next five years, Marchionne said.
Google-parent Alphabet announced an alliance with Fiat Chrysler Automobiles (FCA) in a major expansion of its fleet of self-driving vehicles. The company's test fleet will be more than doubled with the addition of 100 new 2017 Chrysler Pacifica Hybrid minivans, with the companies aiming to have some on the road by the end of this year.
Also read : The connected car revolution is happening out of India for the globe – why we need to seize the moment
The collaboration with FCA marks the first time that the California-based Internet giant has worked directly with an automaker to build self-driving vehicles. Google began testing its autonomous driving technology in 2009, using a Toyota Prius equipped with the tech giant's equipment. It now has some 70 vehicles, including Lexus cars adapted by Google and its in-house designed cars unveiled in 2014.

An array of automobile makers including Audi, Ford, Mercedes, Lexus, Tesla and BMW are working on building self-driving capabilities into vehicles.







