How emerging lending models can help solve the Rs 25 trillion credit gap among MSMEs: Report
The BlinC Invest report reflects that the MSME sector has a total credit demand of Rs 69.3 trillion, growing at a CAGR of 11.5%. with less than 15% of the demand being catered by formal sources. The report identifies the key opportunities while proposing business models best suited to cater to this
The micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSME) sector in India comprises 63.4 million businesses which contribute 30% to India’s GDP. While MSMEs are considered as the backbone of the economy, it struggles with lending challenges majorly in the form of working capital.
The BlinC Invest report reflects that the MSME sector has a total credit demand of Rs 69.3 trillion, growing at a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.5%. with less than 15% of the demand being catered by formal sources. The report identifies key opportunities while proposing business models best suited to cater to this demand.
While quarterly MSME disbursements have grown 2x over the last 2 years, this is primarily on account of increased credit penetration and not on account of additional risk taken by the financial institutions. This is indicated by the fact that approval rates for the medium risk tier segment have remained unchanged, hovering around 30%-35% for private banks in the last one year and have decreased for PSUs and NBFC over the last 2 years.
“Private banks have been at the forefront of lending to MSMEs followed by NBFCs. PSUs with their branch network and NBFCs with their Feet-on-Street network can help further drive financial inclusion in Tier 3/4 towns and villages in the country,” the report mentions.
How new-age lending models are revolutionising the way Indians shop
Unlike the traditional lending models, the report shows nine business models such as payment gateways/QR code, POS financing, Neobanks, P2M Lending, anchor-based supply chain finance etc., which have paved the way for the development of the MSME sector. The total funding garnered into this sector stands at ~$5.5 Bn for the period 2016-2021 with majority of the funding received by neobanks, NBFC with branch network, payment gateway/QR code business models.
Talking about the report, Amit Ratanpal, Founder & MD, BLinC Invest said, “Businesses need funding to grow. The MSME market is largely underserved in terms of financing and solving this huge credit gap is critical to growing the Indian economy as a whole... We hope the report will encourage investment and innovative ideas that will provide this key sector the much-needed funds to grow their businesses.”
The report highlights four white spaces - POS Financing, Anchor-led Supply Chain Finance, NBFC (with branch network), and Embedded Finance. “Improvement in underwriting mechanism for MSMEs by evaluating alternative data will significantly boost the approval rates and in turn overall lending to the segment,” it states.

Image credits: BlinC Invest
What is POS Financing?
Point of sale financing is when the merchant offers their customers a consumer financing solution at the point of purchase.
According to the report, POS terminals have seen a stellar growth over the last few years providing greater ease and convenience to MSMEs. There is 10% of POS penetration in the sector and the number of POS terminals are expected to grow to 7.5 mn by 2025
The report highlights that adoption of POS terminals among merchants can be improved by offering them a integrated POS with features such as payables and receivables management and CRM which could help automate payments and collections and increase footfall with targeted services to customers
Anchor-led Supply Chain Finance help MSMEs with working capital
While sourcing goods, most of the merchants have to pay within 7-15 days as their suppliers don’t provide them enough credit, especially after Covid. The requirement of
MSMEs is working capital whereas the product offered is term loan which does not cover their short-term needs.
“In India, the supply chain finance gap is estimated to be Rs 60,000 Cr with current penetration being less than 1% of,” the report highlights.
The supply chain finance helps them optimize their working capital cycle and also avail cash discount on early payment and the market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 17%, according to the study.
NBFC with branch network
Non Banking Financial Institutions (NBFCs) are a major source of lending for MSMEs. However, the report states that disruptions in business and economic activity amid COVID has constrained NBFCs AUM growth to 2-5% in FY2020 to 2022. It brings out that riding on macroeconomic tailwinds, the AUM is expected to reach a 4-year high of Rs 13 lakh crore by this fiscal.
According to the report, currently, the majority of the NBFCs are focused on the northern states like Rajasthan, Haryana, Delhi-NCR and Uttar Pradesh. There is a large market opportunity for NBFCs to penetrate the eastern states like West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand, Orissa and the
North-Eastern states which are typically not catered to. In terms of products.
Embedded Finance to solve the dilemma
Embedded Finance helps make credit decisions by looking at alternate data as well as platform transactional data. Additionally, they leverage the rich historical and demographic data about MSMEs to understand the heterogeneity of the segment and offer tailored financial products.
The industry reached a size of $4.8 Bn in 2022 and is expected to reach $21.1 Bn by 2029.
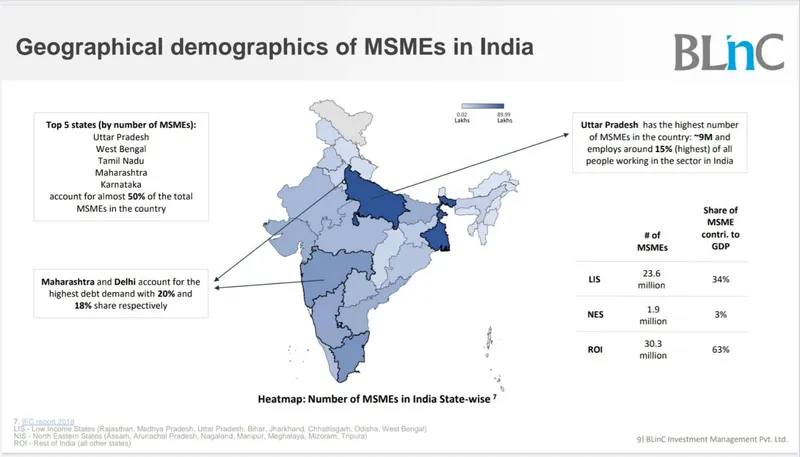
Image credits: BlinC Invest
Speaking to SMBStory, Amit highlighted how PoS and QR Code financing will benefit MSMEs given the digital penetration of MSMEs and their trust towards these financing methods is lower in the semi-urban/rural regions.
“MSMEs are very fragmented in the country making customer acquisition very expensive for financial institutions. With the rapidly strengthening infrastructure including telecom, POS and QR code will solve this problem to a great extent as customer acquisition can be done by installing a QR code or POS terminal and financial institutions can leverage QR code and POS transaction data for credit underwriting," he said.
From the new-age investors perspective, Amit highlights that for any country, MSME is the largest opportunity. In India also, the sector contributes to 30% of the GDP and employs ~111 Mn people comprising ~25% of the working population.
“Lending to MSMEs is a large opportunity and the segment has a credit gap of Rs 25 Tn. The adoption of technology and roll-out of VAS for MSMEs will be a key enabler for the MSME lending segment in the coming years. The segment has garnered a funding of ~USD 5.5 Bn during the period 2016-2021 and continues to be an attractive area for the investors," he says.
Edited by Akanksha Sarma



