
A UX perspective on product design
In the design world, product design and UX design often get confused with each other. The responsibilities are blurred and confused because UX designs have acquired new attributes, thanks to the evolution of the design industry. Let’s delve deeper.
Product Design V/s UX Design – Similarities and Differences
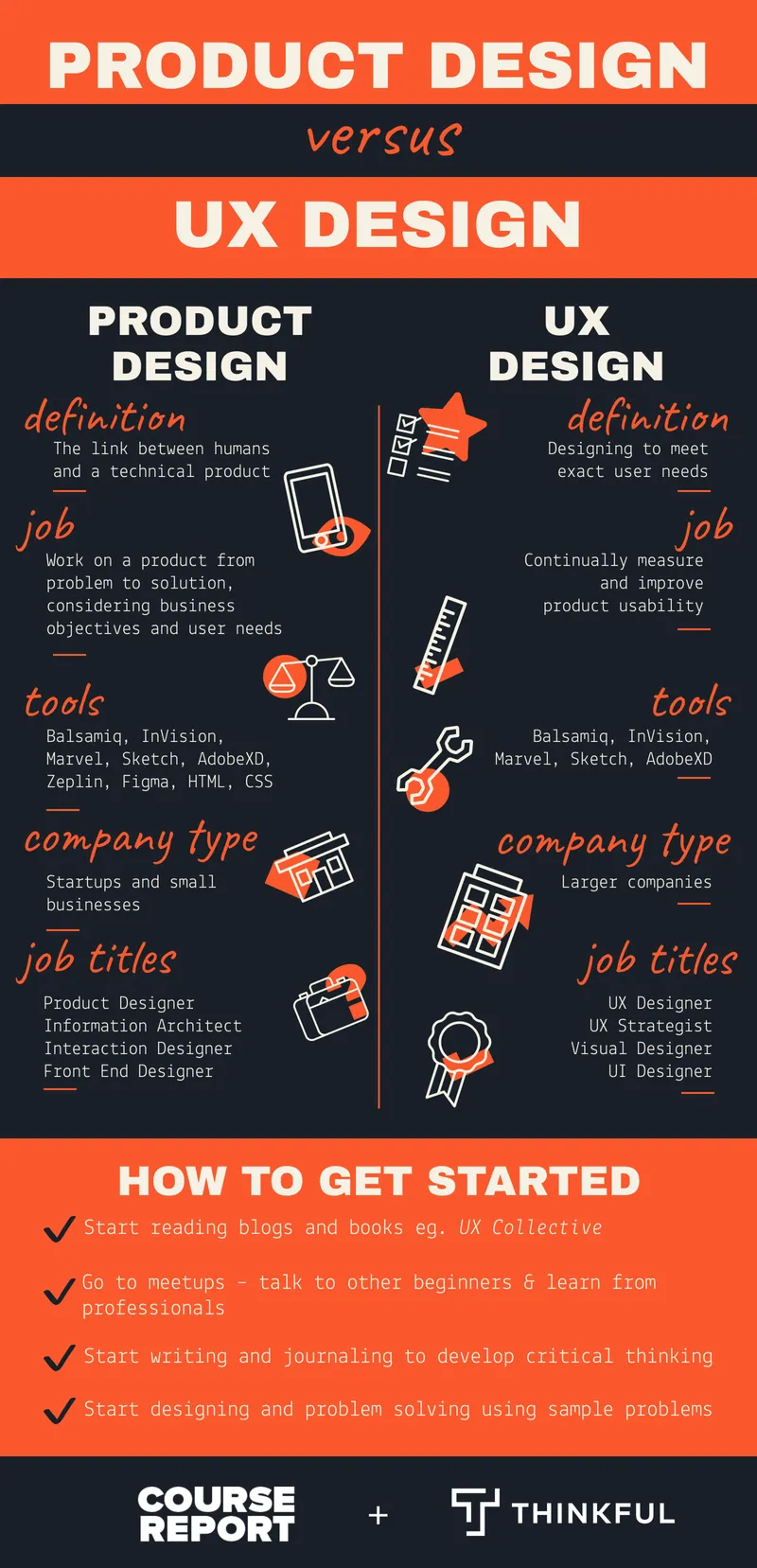
Product design is an integrated approach to developing new products from the start to the end. The process involves market research, defining problems, developing informed solutions, developing the product, and other related tasks. Product designers aim to offer solutions and design user-friendly products and provide a solution for a problem. The responsibility of the designers is to think about the crucial aspects of the product which would lead to the marketing and design success of the product.
On the other hand, designers use UX design to create products that offer meaningful experiences to users. The process involves designing the overall process of acquiring, as well as integrating the product. It also covers aspects of design, branding, function, and usability. UX designers start by asking key questions regarding the product's functionality and think of user motivations for adopting a particular product.
An example of good UX design is Google. The much-loved search engine has been keeping it simple since 1998, translating into 3.5 billion+ searches a day.
Similarities:
- Both require similar designing skills with design thinking at their core.
- Both focus on creating a product that is functional and easy to use for the end-user.
- Data management skills are a necessity because designers have to analyze and quantify data before making a product.
Dissimilarities:
- Product design emphasizes business requirements, and UX design care about users' needs first while incorporating business end goals.
- Product designers are involved in creating the feel and look of a procreating and offer insight into how a product should operate.
- UX designers’ primary concern is how the product feels and builds a prototype interface to track users via testing methods like email surveys and A/B testing.
- UX designers use interactive design tools and wireframe design tools, while product designers use sketch tools and mind mapping tools.
User experience and the product design process – key steps
1. Knowing why you are designing a product and understanding the constraints
Before delving into the design process, a UX designer must know why a product is being designed and the problem it is expected to solve. Understanding the obstacles and resource constraints is also essential to determine the turnaround time and expected deliverables.
Take Amazon, for instance. The company was founded to sell books online and later expanded to sell software, electronics, apparel, toys, food, etc. The website and app exist because they fulfill a need – the convenience of shopping on the Internet.
2. Defining the target audience

The best way to define and understand the target audience is through the creation of user personas. This will help you know your users and figure out how users will be using the product to build solutions according to their needs.
A user persona is an individual profile that is created for various imaginary sets of user groups. Their interests, skills, pain points, frustrations, wants, and needs are defined. This reveals if the product can offer the best solution to the problem that the users are trying to solve.
3. User research and analysis
Is there a need for your product? The answer to this question is vital before commencing the design and development process. Conducting user research and analyzing the data is the best way to validate the product-market fit. You can conduct user research by using any one of the two approaches – behavioral research and attitudinal research. The first is where you observe your users through surveys and other studies, and the latter is listening to what they have to say. Online surveys, user interviews, market research, and contextual inquiry are some of the methods implemented for user research.
The data that has been collected from the research is then assessed to form insights and make informed decisions whether to go ahead with the design project or start a new one that users need.
4. Competitor research
The best way to understand how to design your product or position your product in the market is through competitor research. Analyzing competition offers inspiration and enlightens you of the mistakes that should not be repeated. Also, competitor research helps give ideas about how to stand apart in the industry while essentially offering the same product.
Compare Gett and Uber, for example. Gett allows users to sign up and offers on-demand corporate transportation. Uber also allows users to sign up and offer ride-hailing, courier, and other services. The user journey is quite similar as users have to sign up, log in, book a car, track the driver and make payment. But, the difference between the two is that Gett is out there to transform corporate ground traveling and Uber cater to the traveling needs of anybody in need of a ride.
5. Mapping user journey
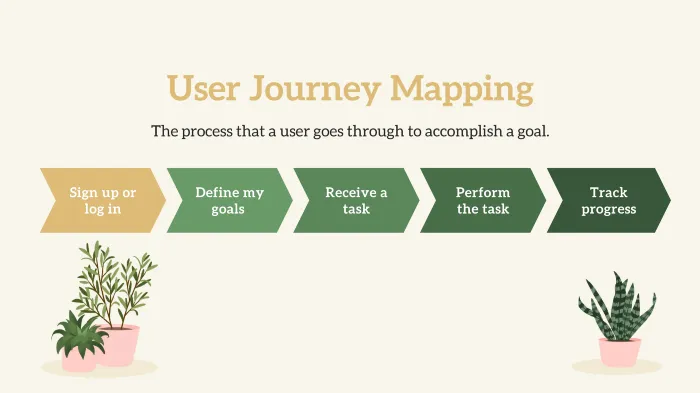
Mapping the user journey involves devising the flow of tasks that you expect users to perform when using the app or web solution. The tasks are created, along with a flow of various kinds of actions that will take place. This helps to give designers a perspective of the product from the users’ POV, and they can check if they’ve added everything in the product.
6. Design ecosystems
Designing ecosystems have always been the primary concern of UX professionals. This is where the information architecture is created, along with the wireframes. Designing ecosystems is truly about designing from the point of view of the users. There are several ways to draw an ecosystem, and many UX professionals even rely on rough sketches or diagrams drawn on a piece of paper before they move on to visual design.
7. Create the prototype
The wireframes are digitized to create the prototype of the product. Sketch, Figma, and Adobe XD are some of the tools used for making the prototype. Animations and other features can also be included. Sometimes, the prototype is released to a select few users to determine if the product has achieved its benchmarks. The prototype can be reviewed, and changes can be made so that the final product that is launched is flawless and up to the user’s expectations. The goal of a prototype is to test products before a lot of money and time is invested in the final product.
8. Usability testing and A/B testing
Usability testing is a crucial part of the design process as it will help you get accurate feedback from users before the product is finally launched or released. It is also good to check the product's usability throughout the creativity and design process so that precious time is not invested in designing something flawed from the start. Also, A/B testing is essential if you are planning to release the product across various digital platforms. It compares two versions of an app or web page against each other to find out which one performs better.
After the testing checks out and the bugs are fixed, it is time to release the product. But, the process doesn’t end there. To improve the experience of the product and make the journey smooth for the users, you need to do the following:
- Gather feedback and conduct a follow-up market research
- Start designing the next update feature
Looking Forward
When designing a product/app/website, the most important thing to consider is the users for whom the product will be designed. This is why UX design plays a crucial role in all kinds of product design tasks and fulfills the ultimate goal of creating a product that satisfies the needs and wants of the end-users.




![Get more Views on YouTube for FREE [Complete Guide]](https://images.yourstory.com/cs/1/c0899f40-0509-11e9-9820-1f4fb7912c4d/Get_more_Views_on_Youtube_complete_guide1561245757751.jpg?mode=crop&crop=faces&ar=1%3A1&format=auto&w=1920&q=75)

