
Delivering Quality: The Seven Key Benefits of Optimising Your Site Using a CDN
Website speed can’t be the only driving force behind implementing a CDN. So what exactly are the benefits of optimising your site with a CDN?
If hosting providers are putting in the work to let you deliver content, run your website and upload videos and images - why bother implementing a CDN solution?
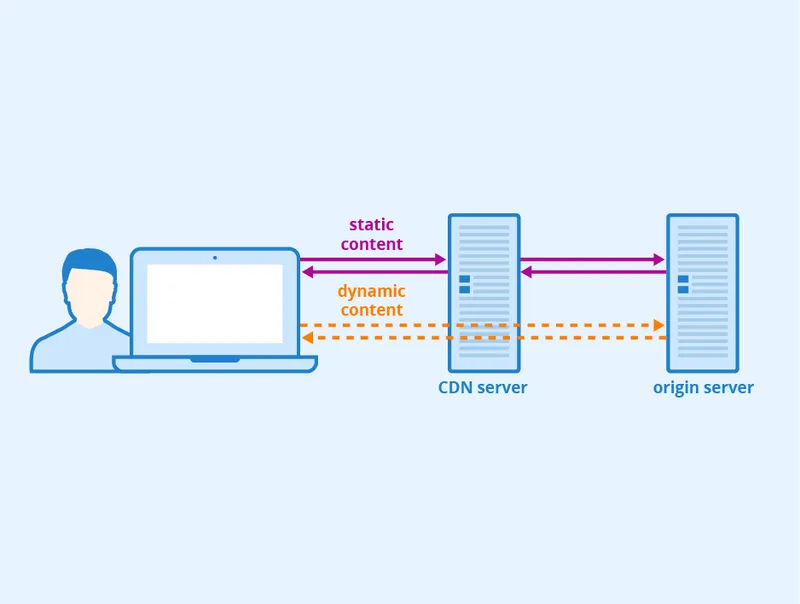
(CDN Mechanism. Image: Source)
A Content Delivery Network is essentially a network of geographically dispersed server nodes for users to download static content like images or JavaScript. Since the CDN is spread far and wide across the world, server nodes are never too far away from users. This reduced latency allows for that all-important speedier response and fast download time of content.
The best part of an end-users page-load time is spent on retrieving structural components of a site like its static content. CDN’s act as building blocks to carry static content on the node closest to the user accessing your site; ensuring the shortest distance for the data to travel.
In 2020, global content delivery network internet traffic is projected to reach 252 EB per month; up from 54 EB less than just three years ago (Statista). The growing importance of businesses online presence has pushed organisations to use CDNs to accelerate content, secure transactions and enhance user-experience.
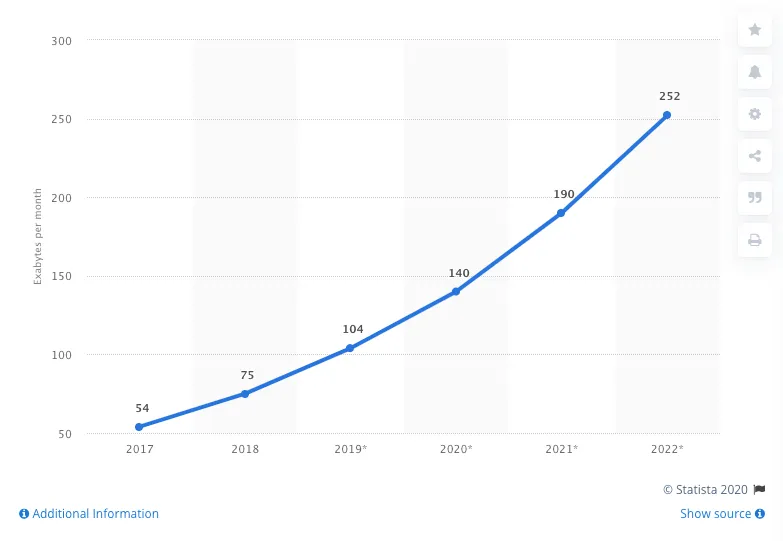
(Data volume of global content delivery traffic. Image: Statista)
Surely, speed efficiencies can’t be the only driving force behind this internationally-approved trend. So what exactly are the benefits of optimising your site with CDN?
Delivery Optimisation
Optimising the delivery of content is necessary to overcome IT silos and eliminate friction between IT and your business goals. Fast, secure and optimised delivery of internet content allows for the quick transfer of assets needed for loading HTML pages, javascript files, stylesheets, images and videos. Optimal configuration of your CDN can also help protect websites against malicious attacks like DDOS attacks.
Website optimisation is inherently determined by the standard of content delivery. Low-performance indicators can often be due to long redirection chains. By resolving redirections at the CDN level, if the origin server attempts to redirect data to some other location, internal resolutions can step in to retrieve the final resource and speed up the delivery process.
Ultimately, content propels businesses forward and carries the important information you want to share with the world. If you’re going to do it; do it right with the right CDN for you.
Content Optimisation
Whilst the method by which content is delivered (quickly and securely) is a fundamental priority for many CDN solutions, there is much to be said for the optimisation of the content itself. CDNs can provide Delivery optimisation but often leaves much of the technical setup on its users.
Some providers like PageCDN and StackPath (previously known as MaxCDN) enable a host of content optimisation services in an all in one solution with a very simple user interface. These tools are ideal for non-developers and are equally usable for more sophisticated web developers.
Such providers allow content across all websites and WordPress, in particular, to be supported by more features than any existing WordPress plugin. Optimising content in the process of delivering it more effectively is key to user experience.
For example, innovative compression mechanisms like Brotli-11 compression gives users the highest possible compression ratio with the simplest of interfaces. Compressing size files results in speedier delivery and better website performance.
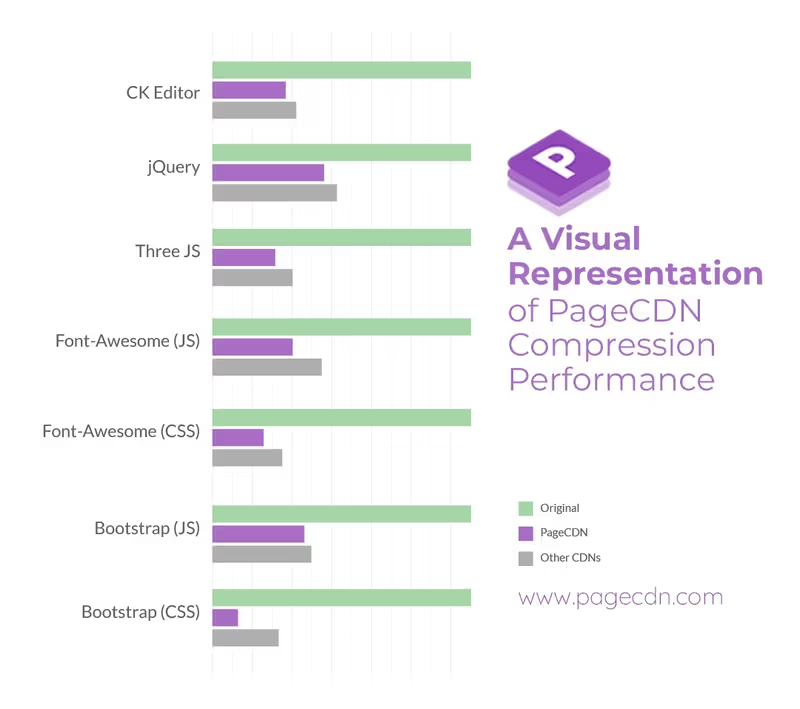
(Compressed file size comparison. Image: Source)
Cache Optimisation
CDN caching is at the forefront of the content delivery network model. Consider how browser caching stores files on a hard drive; where they can be accessed at any point - a CDN effectively moves the content to powerful proxy servers for accelerated content distribution.
Each Point of Presence (PoP) functions as a node in a global network to store and serve an optimised cache for local requests of content. Once stored, it’s retained for easy access upon request. Meaning, unnecessary stress on the origin server is reduced and website performances are strengthened.
1: SEO Benefits
Google loves a fast loading website and page speed is a direct ranking factor. Key indicators of speed come from the following: Server response time, image compression, HTML & CSS structure and cache optimisation.
Amongst other things, these can all be directly optimised by a functional CDN. Meaning, your content delivery optimisation efforts will soon see your site ranking in the top pages of Google and exposed to a wider audience.
2: User Experience
One of the most frustrating things for users is having to wait whilst page loads. May will abort the page and the few that remain will certainly not be pleased with the experience. A CDN is a solution that offers sophisticated and powerful tools to optimise content and content delivery, thereby lifting the responsibilities of your server and generating a better user experience.
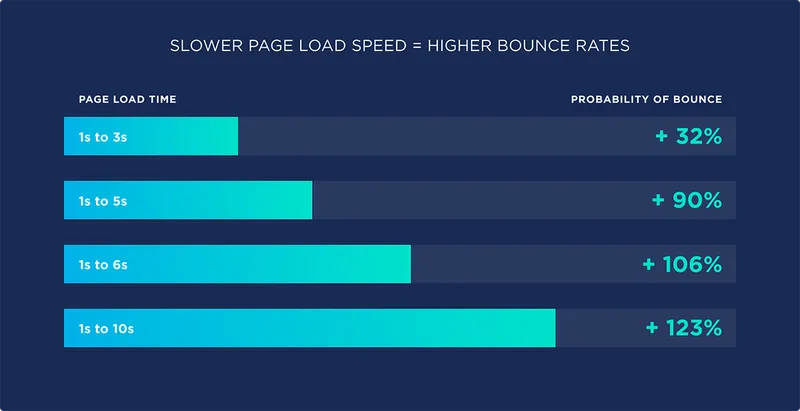
(Bounce Rate by page speed. Image: Source)
By improving user experience, you can expect more return visitors and a direct SEO boost.
3: Security
As more businesses and CDN operators move applications and resources to the cloud, security is a growing concern. CDN security solutions work towards protecting data from loss and theft and fends off third part interruptions that can have lasting effects on website performance and business revenues.
A CDN can help to keep your website safe from Distributed Denial of Service attacks and cyber-exploits. Such attacks can make your entire website inaccessible but a CDN can limit the effectiveness of DDoS attacks by adsorbing it through one of its many edge servers.
4: Reduce pressure from Origin Server
One of the main benefits in optimising your website using CDN is that it alleviates a lot of the workload on the origin server; in turn, boosting efficiencies all round. When millions of users around the world are requesting your origin server at a time, a great deal of stress is put on your server.
A CDN helps to deliver the content requested by users through a distributed network of edge servers. As such, the origin server is freer to deal with actual user-related tasks instead of swamped serving static content.
5: Global Reach
There are 3.4 billion internet users online, meaning the global use of the internet has increased exponentially over the past 20 years. amount of years. CDNs provide solutions to both deal with this demand and allow websites to operate effectively on an international scale.
Through cloud accelerations with local PoPs; latency problems that can interrupt long-distance data transactions, slow downloading times are minimised. For example, a website might be hosted in a particular region, but have the majority of its users in a completely different location.
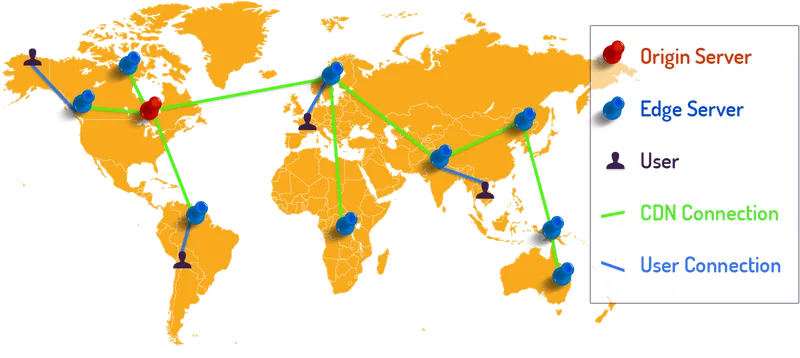
A website hosted in North America might report good speeds based on a default test location. But when most users are on the other side of the world, their speed will not be to the standard’s experienced in North America. A CDN, therefore, allows users from any point of origin to download static content from a closer edge server. By enabling a high traffic flow, a CDN allows people from around the world to access your website simultaneously.
6: Access to Analytics
CDNs can offer priceless analytical information that can reveal the strengths and weaknesses of online business and can be used in marketing pursuits going forward. These networks have the capacity to deliver real-time load statistics, optimise capacity per customer, display active regions and indicate popular content.
This information analysis shows everything a developer needs to make further optimisations to the website. So, such in-depth reporting on key metrics and user-activity ultimately lead to better performance and subsequently higher user experience. The end result should have a noticeable impact on sales and conversion rates.
7: Cache Sharing Benefits
A public CDN allows many websites to share the same resource. This provides free bandwidth and the option to automatically load the latest versions as they are made available by others. It also allows multiple websites to share the same HTTP cache of the same resource. Making it much faster to download your website pages.
This is even true for first-time visitors, provided that some of your website resources are already available in the browser cache of another website that the user visited.







